
|
|
Code /
MMPP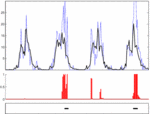 OverviewThis code implements a Markov-modulated Poisson process model for learning patterns of periodic activity in count-based sensors, and detecting aperiodic events (deviations from the normal pattern). We use a discrete-time model, in which the data are modeled as consisting of the superposition of "normal" behavior, represented using a Poisson process, and "event" behavior consisting of increases (or more rarely, decreases) in the number of counts observed. The event behavior is captured using a Markov chain model to capture the idea of event persistence, allowing the model to find slight but sustained changes in activity and more accurately estimate the duration of a detected event. An example is shown at right, where the blue curve shows the observed counts, black the estimated normal profile; red bars show the estimated probability of an event at each time, and the bottom-most panel shows a partial ground truth of known events, held out from the model for validation purposes. See our relevant publications:
 DataData used in our experiments are available from the UCI Machine Learning Repository:
CodeKDD-06 -- Positive events only CopyrightAll code is copyrighted and licensed under the LGPL (Gnu lesser general public license). It comes with absolutely no warranty or guarantees of any kind. |